Therapeutic Application of Carvacrol: A Comprehensive Review
Therapeutic Application of Carvacrol: A Comprehensive Review (Thymol and Oregano Oil potential antimicrobial, anticancer, cancer fighting, anti inflammatory)
Carvacrol is a major natural constituent and is significantly present as an essential oil in oregano and is well known for its numerous biological activities. Therapeutic applications of carvacrol have been demonstrated as anti‐oxidant, anticancer, cancer fighting, diabetes prevention, cardioprotective, anti‐obesity, hepatoprotective and reproductive role, antiaging, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory properties.

Abstract
Carvacrol is a major natural constituent and is significantly present as an essential oil in aromatic plants and is well known for its numerous biological activities. Therapeutic properties of carvacrol have been demonstrated as anti‐oxidant, anticancer, diabetes prevention, cardioprotective, anti‐obesity, hepatoprotective and reproductive role, antiaging, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory properties. The carvacrol biosynthesis has been mediated through mevalonate pathway. Carvacrol has the anticancer ability against malignant cells via decreasing the expressions of matrix metalloprotease 2 and 9, inducing apoptosis, enhancing the expression of pro‐apoptotic proteins, disrupting mitochondrial membrane, suppressing extracellular signal‐regulated kinase 1/2 mitogen‐activated protein kinase signal transduction, and also decreasing the phosphoinositide 3‐kinase/protein kinase B. It also decreased the concentrations of alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase and aspartate aminotransferase, and gamma‐glutamyl transpeptidase as well as also restored liver function, insulin level, and plasma glucose level. Carvacrol also has been found to exert antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Coagulase‐negative staphylococcus, Salmonella spp., Enterococcus sp. Shigella, and Escherichia coli. The current review article summarizes the health‐promoting perspectives of carvacrol through various pathways.
Carvacrol is a major natural constituent in applauded for their nutraceutical potential ranging from antioxidant to anticancer
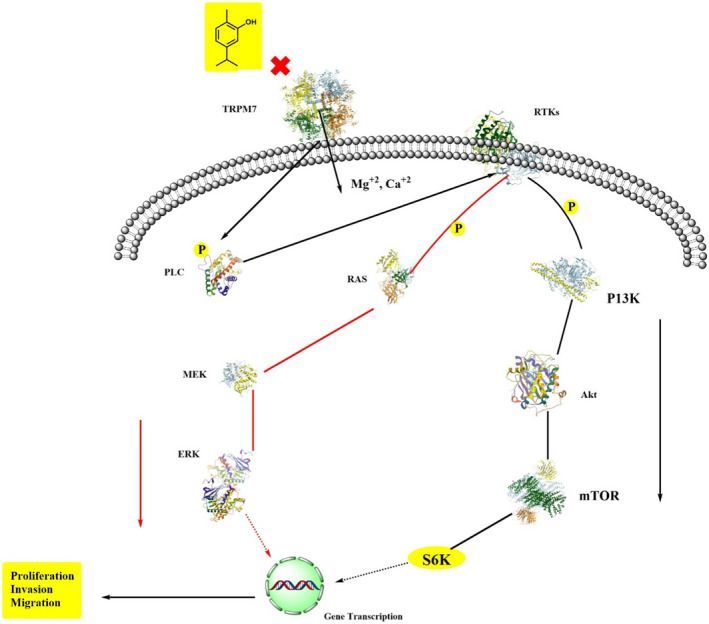
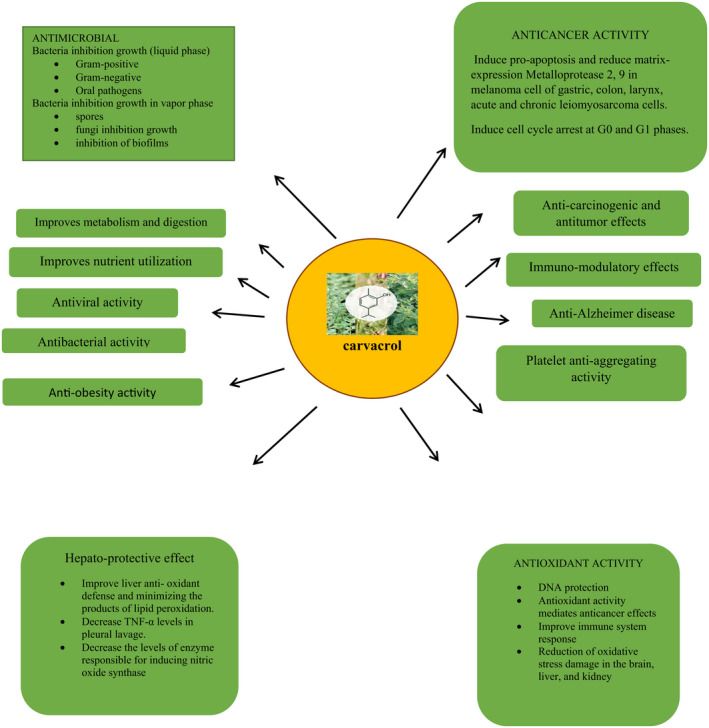
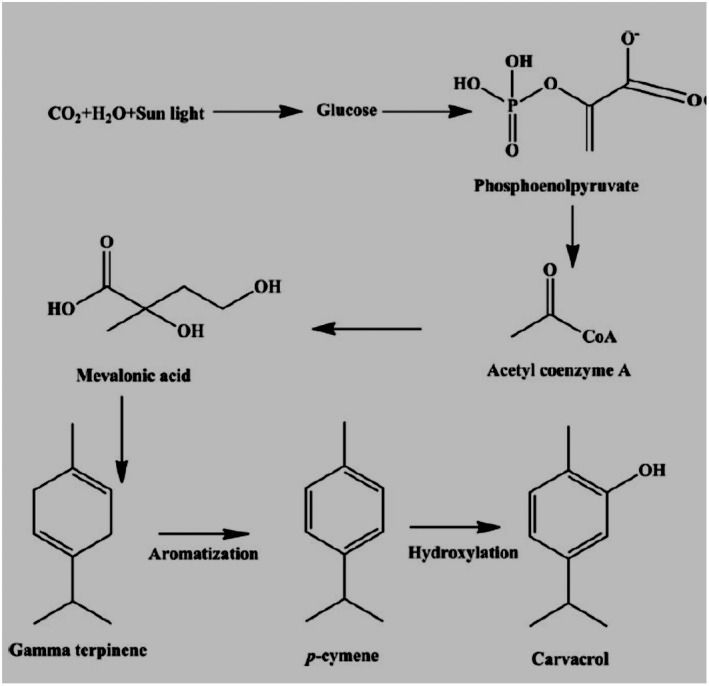
FIGURE 1: Carvacrol biosynthetic pathways via the mevalonate pathway.
1. Introduction
Carvacrol (2‐Methyl‐5‐[1‐methyl ethyl]‐phenol) is a naturally occurring phenolic monoterpenoid and cymene derivative. Its chemical formula is C6H3CH3 (OH) (C3H7) and is naturally present in thyme (Thymus vulgaris), wild bergamot (bergamia Loise var. Citrus aurantium), Origanum scabrum, black cumin, Origanum microphyllum, Origanum onites, oregano (Origanum vulgare), and pepperwort (Lepidium flavum). Carvacrol oil extracted from thyme is 5%–75%, whereas 50%–70% oil is extracted from the marjoram and hop marjoram (Ares et al., 2020; Churklam et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2020; Tampau et al., 2020).
Its boiling point is 237–238°C (lit.) and it melts at 1°C (lit.). The density of carvacrol is ranged from 0.976 g/cm3 at 20°C to 0.975 g/cm3 at 25°C. It is not soluble in water but highly soluble in ethanol, carbon tetrachloride, and diethyl ether (Alagawany et al., 2015; Churklam et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2020; Mousavi et al., 2020). Biological activities of carvacrol have been shown in different in vivo and in vitro studies including anti‐oxidant, antiseptic, anticarcinogenic, anti‐inflammatory, antidiabetes role, immunomodulatory, antimicrobial activity, antispasmodic, antibacterial, and growth promoter. As it is a natural cymene derivative, it has potent bacterial inhibiting abilities and due to its flavoring property used in food industry as a preservative (Churklam et al., 2020; Memar et al., 2017; Mousavi et al., 2020; Rezvi & Roy, 2019; Scaffaro et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2020).
Ezz‐Eldin et al. (2020) showed the antiproliferative, anti‐inflammatory, and pain‐relieving properties of carvacrol against bronchial asthma; bronchial asthma in animals was induced by an intranasal dose of ovalbumin. IN serum absolute eosinophil count (AEC) and immunoglobulin E (IgE) and inflammatory biomarkers like IL‐3, IL‐4, IL‐5, IL‐13, TNF‐α, IFN‐γ, and iNOS were determined in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. The level of oxidative stress biomarkers was also measured. Results determined that carvacrol is a significant anti‐oxidant and antiproliferative agent (Ezz‐Eldin et al., 2020). Plants synthesized carvacrol via the mevalonate pathway. Glucose is first decarboxylated and acetylated to acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA), which could then be turned into mevalonic acid. Aromatization converts mevalonic acid to gamma‐terpinene, which is then converted to p‐cymene. Carvacrol was produced by the hydroxylation of p‐cymene, as shown in Figure 1.
2. Therapeutic Perspectives
Carvacrol (2‐Methyl‐5‐[1‐methyl ethyl]‐phenol) is a naturally occurring phenolic monoterpenoid and cymene derivative. Its chemical formula is C6H3CH3 (OH) (C3H7) and is naturally present in thyme (Thymus vulgaris), wild bergamot (bergamia Loise var. Citrus aurantium), Origanum scabrum, black cumin, Origanum microphyllum, Origanum onites, oregano (Origanum vulgare), and pepperwort (Lepidium flavum). Carvacrol oil extracted from thyme is 5%–75%, whereas 50%–70% oil is extracted from the marjoram and hop marjoram (Ares et al., 2020; Churklam et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2020; Tampau et al., 2020).
Its boiling point is 237–238°C (lit.) and it melts at 1°C (lit.). The density of carvacrol is ranged from 0.976 g/cm3 at 20°C to 0.975 g/cm3 at 25°C. It is not soluble in water but highly soluble in ethanol, carbon tetrachloride, and diethyl ether (Alagawany et al., 2015; Churklam et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2020; Mousavi et al., 2020). Biological activities of carvacrol have been shown in different in vivo and in vitro studies including anti‐oxidant, antiseptic, anticarcinogenic, anti‐inflammatory, antidiabetes role, immunomodulatory, antimicrobial activity, antispasmodic, antibacterial, and growth promoter. As it is a natural cymene derivative, it has potent bacterial inhibiting abilities and due to its flavoring property used in food industry as a preservative (Churklam et al., 2020; Memar et al., 2017; Mousavi et al., 2020; Rezvi & Roy, 2019; Scaffaro et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2020).
Ezz‐Eldin et al. (2020) showed the antiproliferative, anti‐inflammatory, and pain‐relieving properties of carvacrol against bronchial asthma; bronchial asthma in animals was induced by an intranasal dose of ovalbumin. IN serum absolute eosinophil count (AEC) and immunoglobulin E (IgE) and inflammatory biomarkers like IL‐3, IL‐4, IL‐5, IL‐13, TNF‐α, IFN‐γ, and iNOS were determined in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. The level of oxidative stress biomarkers was also measured. Results determined that carvacrol is a significant anti‐oxidant and antiproliferative agent (Ezz‐Eldin et al., 2020). Plants synthesized carvacrol via the mevalonate pathway. Glucose is first decarboxylated and acetylated to acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA), which could then be turned into mevalonic acid. Aromatization converts mevalonic acid to gamma‐terpinene, which is then converted to p‐cymene. Carvacrol was produced by the hydroxylation of p‐cymene, as shown in Figure 1.
FIGURE 2: Anti‐oxidant potential of carvacrol.
FIGURE 3: Health perspectives of carvacrol.
2.2. Anticancer activity
Carvacrol has anticancer ability against malignant cells via decreasing the expressions of matrix metalloprotease 2 and 9 (Bayir et al., 2019; Fan et al., 2015; Rezvi & Roy, 2019). Its antiproliferative activities induce apoptosis, which further increases the expression of pro‐apoptotic proteins. In cancer cells lines JAR and JEG3 cells, carvacrol induces calcium ions burden in the mitochondrial matrix via disrupting the mitochondrial membrane, suppresses extracellular signal‐regulated kinase 1/2 mitogen‐activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal transduction, also decreases the phosphoinositide 3‐kinase/protein kinase B, and increases phosphor‐P38 and c‐Jun N‐terminal kinase MAPK expressions (Chraibi et al., 2020; Lim et al., 2019). Carvacrol in normal cells (L92) was also found to induce apoptosis via mitochondrial membrane potential disruption, ROS generation, activation of caspase3, and DNA damage (Jamali et al., 2020). A study conducted by Fan et al. explored that carvacrol works as an anticancer agent in different human colon cell lines such as LoVo and HCT116 via decreasing the matrix metalloprotease 2 and 9, cell‐proliferation, cyclin B1 expression, and In causing In cell In cycle arrest at G2 and M phases. Additionally, it also increased phosphorylation of the extracellular‐regulated protein kinase B and downregulated Bcl‐2 expression (Fan et al., 2015). It also exhibited the dose‐dependent inhibition in tumor growth cells in prostate cancer cells (PC3 cells) (Trindade et al., 2019). In a study, carvacrol‐encapsulated nanoemulsion (CEN) formulated by a combination of polysorbate 80, lecithin, and MCT in lung A549 cells line in a dose‐dependent manner reduced the activation of MAPK, p38, and ERK and decreased the expression of CD31 and VEGF (Carvalho et al., 2020; Khan, Bhardwaj, Shukla, Lee, et al., 2019; Khan, Bhardwaj, Shukla, Min, et al., 2019; Khan, Singh et al., 2019). Carvacrol can inhibit prostate cancer progression by inducing programmed cell death and cell cycle arrest at G0 and M‐phases. In a dose‐ and time‐dependent manner, carvacrol exhibited protective effects against prostate cancer cells via lowering cell viability, increasing the rate of reactive oxygen species, and disrupting the mitochondrial membrane potential. Carvacrol induced cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 that declined increased CDK inhibitor p21 expression and decreased cyclin‐dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), and cyclin D1 expressions. Moreover, carvacrol inhibited Notch signaling in PC‐3 cells via downregulating Jagged‐1 and Notch‐1 (Karam et al., 2019).
Heidarian examined the dose‐dependent effects of carvacrol in human prostate cancer cell lines, which significantly reduced IL‐6 gene expression as compared to the control group in which IL‐6 protein reduced 41.5% and 52.7% at 360 and 420 μM. Carvacrol reduced cellular signaling proteins and gene expression and cellular signaling proteins. Further, it also caused a reduction in the cell survival rate, invasion, and proliferation rate (Bayir et al., 2019; Heidarian & Keloushadi, 2019). A study reported by Pakdemirli et al. in 2020 examined carvacrol effects on both HT‐29 and HCT‐116 via lowering the survival rate and proliferation rate (Pakdemirli et al., 2020). In different in vitro and in vivo studies of MDA‐MB 231 cells, carvacrol‐induced apoptosis lowered the mitochondrial membrane potential resulting in the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, cleavage of PARP, and caspase activation (Arunasree, 2010). Certain available evidence showed that carvacrol has cell cycle G2 arresting ability against hepatic cancer cells via enhancing cell apoptosis, activation of the caspase‐3, cleavage of PARP, and decreasing gene expression of Bcl‐2. Carvacrol dose‐dependently lowers ERK1/2posphorylation, activates phosphorylation of p38, and alters the phosphorylation of the MAPK (Elshafie et al., 2017; Suntres et al., 2015; Yin et al., 2012). Same findings were discovered by Khan, Bahuguna et al. (2017), Khan, Khan, Ahmad et al. (2017) and Khan, Khan, Farooqui et al. (2017), who investigated that carvacrol in human prostate cancer cell lines induced apoptosis and exhibited cell cycle arrest at G0 and G1phases (Khan, Khan, Farooqui et al., 2017). Similarly, Khan, Bahuguna et al. (2017) found the dose‐ and time‐dependent effects of carvacrol on DU145 cells. Carvacrol induced apoptosis by nuclear condensation, caspase‐3 activation, and Annexin V‐FITC/PI‐positive cells. It disrupts the mitochondrial membrane potential and caused cell cycle arrest at G0 and G1 (Khan, Bahuguna et al., 2017).
Carvacrol has significant protective effects in reducing the side effects of chemotherapeutics such as irinotecan hydrochloride anticancer drugs that cause induction of intestinal mucositis. Irinotecan hydrochloride triggers inflammation and leads to cell‐damaging by the transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, and member 1 receptor. Carvacrol reduced inflammatory biomarkers, such as nuclear factor κB and cyclooxygenase‐2, and levels of Nitric oxides, malondialdehyde, and glutathione create oxidative stress. It also acts as an agonist of the transient receptor potential cation channel (Alvarenga et al., 2016). In human cervical cancer HeLa cells, Potočnjak studied the anticancer role of carvacrol against human cervical cancer HeLa cells via decreasing the cell viability, inducing apoptosis, and inhibiting the mitogen‐activated protein kinase (Potočnjak et al., 2018; Zeytun & Özkorkmaz, 2021).
Carvacrol was found to have antitumor, antiproliferative, and apoptotic activity against human colon cancer cell lines LoVo and HCT116 when combined with thyme (Fan et al., 2015). Carvacrol decreased cancer cells proliferation and apoptosis via decreasing matrix metalloprotease (MMP‐2, MMP‐9) expressions while downregulating the Bcl‐2 expression and inducing phosphorylation of extracellular regulated protein kinase and protein kinase B(p‐Akt) at the molecular level (Fan et al., 2015).
Figure 4 depicts a model of the anticancer mechanism of carvacrol.
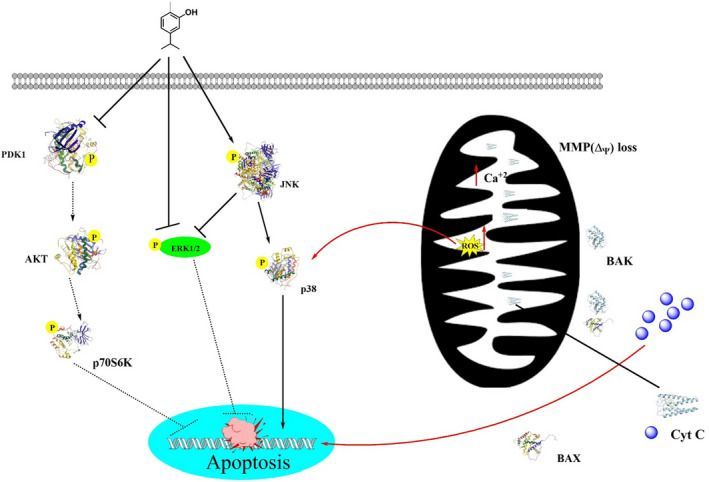
As posted at www.ncbi.nim.nih.gov
As mentioned above, several factors affect the composition of EOs of the oregano species. As the chemical composition of the EOO is directly related with their biological activities, the next section of this review will be focused on such activities.
2.4. Anti‐obesity effects
De novo lipogenesis is the process of formation of new adipose cells derived from the ChREBP transcription factor. In this process, white adipocytes are engaged by one large fat droplet. Spalletta et al. (2018) investigated that carvacrol inhibited fat accumulation in humans 30% in Wharton' jelly‐derived mesenchymal stem cells and 40% in murine 3T3‐L1 cells. In addition, it also reduced autophagy and ChREBP expression (Spalletta et al., 2018).
Carvacrol can control obesity by inhibiting intracellular fat accumulation and adipocyte differentiation as evidenced in high‐fat‐diet‐induced male C57BL/6N mice embryo 3T3‐L1 cells and the mechanism involved in gene expression in thermogenesis, adipogenesis, and inflammation. Carvacrol inhibited visceral adipogenesis through suppression of bone morphogenic protein‐, galanin‐mediated signaling, and fibroblast growth factor‐1. Carvacrol inhibited toll‐like receptor (TLR2 and TLR4)‐mediated signaling and improved pro‐inflammatory cytokines formation in visceral adipose tissues (Cho et al., 2012). Carvacrol in combination with rosiglitazone on diabetic mice C57BL/6J showed a reduction in triglycerides, low‐density lipoproteins cholesterol, total cholesterol, phospholipids, and free fatty acids (Ezhumalai et al., 2015). A study conducted by Umaya and Manpal found that carvacrol has an anti‐obesity role on embryo 3T3‐L1 cells via lowering fat deposition in cells and visceral fats and also improving free fatty acids, liver cholesterol, and HDL‐cholesterol. Carvacrol reduced adipogenesis‐related gene fibroblast growth factor receptor in visceral adipose tissues and galanin receptor 1 and 2 expressions (Suganthi & Manpal, 2013). In a high‐fat‐induced C57BL/6J mice study, carvacrol (20 mg/kg BW) used in combination with thiazolidinediones and rosiglitazone lowered the plasma glucose level, increased hemoglobin level, and increased as well as also alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, and aspartate aminotransferase and gamma‐glutamyl transpeptidase (Ezhumalai et al., 2014). In addition, carvacrol (25 and 50 mg/kg) was supplemented to streptozotocin‐induced diabetes rats for 7 days and found that carvacrol significantly reduced the level of glucose, serum total cholesterol, and body weight changes (Amiri & Akbari, 2018).
2.6. Anti‐inflammatory effects
In asthma, airway inflammation can be suppressed by peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor‐alpha (PPAR‐α) agonists as it reduces the release of inflammatory mediators majorly involved in asthma (Gholijani et al., 2016; Rolim et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2020). Carvacrol protects from intestinal mucositis as it acts as an agonist of transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1(TRPA1). Alvarenga et al. (2016) determined anti‐inflammatory actions via activating the TRPA1 in intestinal mucositis induced by irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT‐11) at 75 mg/kg. It lowered MPO, NF‐ κB, C‐2 receptor, and production of pro‐inflammatory cytokines and lowered the malondialdehyde and nitric oxide level. It also restored villi architecture in the small intestine and side by side improved the blood bacterial count, leukogram, body mass variation, and survival rate. Carvacrol also significantly reduced nitric oxide, lipid peroxides, interleukin‐1 beta, and myeloperoxidase (Alvarenga et al., 2016; Arigesavan & Sudhandiran, 2015). Carvacrol also significantly reduced nitric oxide, lipid peroxides, interleukin‐1 beta, and myeloperoxidase (Arigesavan & Sudhandiran, 2015). Somensi et al. (2019) investigated the molecular pathways of carvacrol action on LPS‐mediated pro‐inflammatory activation of RAW 264.7 macrophages. Preincubation with 100 μM carvacrol prevented ERK1/2 phosphorylation and inhibited NF‐kB (p65) translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus, but it showed no response on p38 and JNK activation (Somensi et al., 2019).
Banik et al. (2019) explored the anti‐inflammatory and antitoxic effects of carvacrol and that it reduced oxidative damage in PC12 cells due to cadmium against caspase‐dependent and apoptosis‐independent pathways. Carvacrol exposure increased glutathione reductase expressions and cellular level of glutathione as well as ameliorated DNA fragmentation magnitude caused by cadmium. Carvacrol improved nuclear factor kappa‐light‐chain‐enhancer of activated B cells (NFКB), downregulation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), protein kinase B (Akt), and extracellular signal‐regulated kinase‐1 (ERK‐1). Carvacrol also suppressed the cleavage of caspase 3, reduced the apoptosis‐inducing factor (AIF) and cytosolic levels of cytochrome c, and increased the intracellular metallothionein content (Banik et al., 2019). A group of researchers and investigators determined the protective effects of carvacrol against cisplatin resistance in HeLa cells via ERK1/2‐dependent autophagy. Both compounds increased cisplatin‐induced light chain 3 beta expressions enhanced by MEK inhibition (Potočnjak et al., 2018).
Therapeutic effects of carvacrol (75 mg/kg) were studied by Zeytun and Özkorkmaz in 2021 against inflammation of Wistar albino rats and induced positive caspase 3 expression within apoptotic cells of the epithelial layer and connective tissues. Carvacrol increased mitotic activities and degenerative changes. Vascular endothelial growth factor was also seen in the papillary region of epithelium and also dilated vascular endothelial cells (Ezz‐Eldin et al., 2020). Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the inflammation of the joints and carvacrol has been proved by different studies that it can reduce inflammation in fibroblast‐like synoviocytes. A study conducted by Li et al. in 2019 showed that carvacrol inhibited LPS‐induced inflammation, cell proliferation, and migration in rheumatoid arthritis‐induced fibroblast‐like synoviocytes. Carvacrol decreased the production of inflammatory cytokines, as well as matrix metalloprotease such as MMP‐1, MMP‐3, and MMP‐13. Moreover, it also inhibited the activation pathways of TLR4/MyD88/NF‐κB, p38, and ERK1/2, respectively (Li et al., 2019). Encapsulated carvacrol in bovine serum albumin (BSA) is used to examine its therapeutic and immunomodulatory effects in adjuvant‐induced arthritis (AIA) in Sprague Dawley rats. Carvacrol‐loaded BSA nanoparticles significantly decreased clinical severity score, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, nitric oxide production, and interleukin (IL)‐17 gene expression (Gholijani et al., 2020).
Carvacrol modulates the neuro‐transmitter pathways, such as serotoninergic, dopaminergic, and γ‐amino butyric acid use in the release and production of inflammatory mediators (Bayir et al., 2019; Lima et al., 2017; Rezvi & Roy, 2019; Sharifi‐Rad et al., 2018).
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Essential Oils of Oregano Species
Inflammation is a normal biological response of the body to tissue damage, infections and chemical or physical agents [120]. During inflammation the production of inflammatory mediators is triggered. Examples of these mediators are cytokines, prostaglandins, enzymes, nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS), among others [121]. If inflammation is not controlled the pro-inflammatory mediators are overproduced which might induce pathologic processes related to diseases such as arthritis, atherosclerosis and cancer to name a few [122,123]. Consequently, inhibition of the mediators is an imperative goal to treat inflammatory diseases.
There is evidence that mention that EOO have the ability to exert anti-inflammatory activity. For example, Leyva-López et al. [16] demonstrated that terpenes, such as thymol and carvacrol acetate, obtained from the three Mexican oregano species, L. graveolens, L. palmeri and H. patens reduced significantly the levels of ROS and NO produced by RAW 264.7 macrophage cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Furthermore, EOs of O. majorana (10 μg/mL) reduced the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-6 in LPS-activated THP-1 human macrophage cells [124]. Recently, Han and Parker [125] showed that EOs obtained from O. vulgare significantly inhibited the levels of the inflammatory biomarkers monocyte chemoattractan protein-1 (MCP-1), the vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and the intracellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) on activated-primary human neonatal fibroblasts. These findings suggest that the EOO have anti-inflammatory properties.
The individual components of EOs of oregano have also been studied to better understand their effect on inflammation. For example, Lima et al. [126] demonstrated that carvacrol exerts anti-inflammatory activity on a typical mice inflammation model. When carvacrol was administrated to mice (at 50 and 100 mg/kg), presenting paw edema, the levels of IL-1β and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) prostaglandins were diminished. The reduction on the mRNA expression of IL-1β and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) might be responsible for the effects mentioned. On the other hand, the levels of the cytokine IL-10 in the swollen paw were improved by carvacrol. So, the anti-inflammatory effect of carvacrol is due to the reduction of pro-inflammatory mediators but also to the increasing of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10) [126]. Carvacrol has also showed the ability to prevent obesity in mice by modulating expression of genes involved in inflammation [127] and to attenuate induced liver injury and ulcer in rats [128,129]. Other EOs components, such as p-cymene [130] and β-caryophyllene [131,132,133,134] have also demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties.
The studies mentioned above indicate that diverse oregano species might be used as anti-inflammatory agents and could be used in formulations for the prevention or the treatment of inflammation-related diseases. Nevertheless, and since the EOO might exert toxic effect on cells, several in vivo and clinical studies are needed before the EOs can be used as an alternative to treat inflammation.
2.8. Neuroprotective role
The neuroprotective role of carvacrol was examined by Guan et al. in 2019 against ischemic stroke, leading to hippocampal neuron damage and impairment in gerbils brain tissue improved. Carvacrol decreased levels of lipid peroxide, reduced cell death, and increased the expression of glutathione peroxidase 4 inhibited by ferroptosis (Guan et al., 2019). In recent findings, Raeini et al. (2019) evaluated that carvacrol has a significant ability to reduce neuronal necrosis and malondialdehyde (MDA) and elevated the levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase activities in the hippocampus of 48 male Wistar rats. Carvacrol improved cognitive functions, spatial learning, and memory capacities (Raeini et al., 2019). Carvacrol deters transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7), which involved in the homeostasis of calcium and zinc. A study investigated the neuroprotective effects of carvacrol 50 mg/kg on cerebral ischemia through blockade of zinc influx on 8‐week‐old male Sprague–Dawley rats. Furthermore, carvacrol decreased oxidative damage, microglial activation, number of degenerating neurons, and zinc translocation through downregulating TRPM7 channels (Hong et al., 2018).
Zotti et al. (2013) documented that the administration of 12.5 mg/kg of carvacrol has an impact on neurochemistry and behavioral outcome in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of animal models, which increased serotonin and dopamine levels. Likewise, 450 mg/kg of carvacrol significantly reduced dopamine in the hippocampus of animals. Results suggested that it is a potent brain‐activating molecule that modulates neurotransmitters and neuron activities (Zotti et al., 2013). The peripheral neuro‐degenerative process is considered important for regenerating peripheral nerves genetically or mechanically. Carvacrol regulates transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1), TRP melastatin M7 (TRPM7), TRP canonical 1 (TRPC1), and TRP vanilloid 3 (TRPV3). A study investigated the regulatory effect of carvacrol on TRPM7‐dependent neurodegenerative process carvacrol specificity Schwann cells. Carvacrol significantly suppressed the morphometric indices, such as myelin, stripe, ovoid, and neurofilament indices. Moreover, carvacrol inhibited TRPM7 upregulation in Schwann cells and protected against the peripheral neurodegenerative process (Chun et al., 2019).
Carvacrol also protects from 6‐hydroxydopamine‐induced neurotoxicity as evidenced by various studies on Parkinson's disease; Manouchehrabadi et al. (2019) investigated the neuroprotective effects of carvacrol on Parkinson's disease models in in vitro and in vivo experiments. In in vitro experiment, post‐treatment carvacrol protects the adrenal pheochromocytoma PC12 cells of animals from 6‐hydroxydopamine‐induced neurotoxicity by toxicity induced by a reduction in intracellular reactive oxygen species, increasing cell viability and reduced intra‐cellular lipid In peroxidation In and In annexin In positive In cells In. Additionally, carvacrol protects against neurodegenerative diseases as it improved catalepsy, akinesia, bradykinesia, locomotor activity, and motor coordination. It also reduced the apo‐morphine, decreased the level of malondialdehyde, and increased the level of reduced glutathione content (Manouchehrabadi et al., 2019).
2.9. Hepatoprotective and gastroprotective role
Carvacrol protects from hepatotoxicity caused by D‐galactosamine (D‐GalN). It suppresses the CYP2E1 and upregulates PPAR‐α, mRNA, and protein expressions (Alagawany et al., 2015; Aristatile et al., 2014; Jamali et al., 2020). Carvacrol also reduces restraint stress induced by chronic exposure to oxidative stress leading to tissue damage in the brain, liver, and kidney. A study indicated that carvacrol prevents oxidative damage and restraint stress. Carvacrol was administered systemically for 21 days in animals and the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) decreased glutathione, SOD, restraint stress, glutathione peroxidase, and glutathione reductase measured in the brain, liver, and kidney of animals. Results showed that in stressed animals' MDA, the level was higher and the levels of GSH and anti‐oxidant enzymes were significantly lower (Samarghandian, Azimi‐Nezhad et al., 2016; Samarghandian, Farkhondeh et al., 2016).
Another study investigated 15 mg/kg of carvacrol's protective effects on age‐associated changes in the action of anti‐oxidant enzymes and levels of lipid per‐oxidation at different ages (2, 10, 20 months) of rats. Results showed more improvement in the actions of anti‐oxidant enzymes of 20 months old rats and carvacrol helped in decreasing lipid peroxidation of 10 and 20 months old rats (Samarghandian, Azimi‐Nezhad et al., 2016). Carvacrol effects on acute pancreatitis (AP) induced by cerulean in animal models analyzed by Bakir et al. in 2016 showed the dose‐dependent manner of carvacrol decreased pancreatitis‐induced malondialdehyde and 8‐hydroxydeoxyguanosine levels as it improved the levels of anti‐oxidant enzymes and decreased the levels of AST, ALT, and LDH (Bakır et al., 2016). Carvacrol also treats cisplatin‐induced acute kidney injury via suppression of ERK and activating PI3K/Akt. Renal oxidative stress increased the expression of 4‐hydroxynonenal, 3‐nitrotyrosine, cytochrome P450 E1 (CYP2E1), heme‐oxygenase‐1 (HO‐1) and expressions of phosphorylated nuclear factor‐kappaB p65 and tumor necrosis factor‐α in animal. The results indicated that acute renal injury suppressed oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation through the modulation of the ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways (Potočnjak & Domitrović, 2016).
A study conducted by Shanmugam et al. in 2019 indicated that carvacrol actions on liver tissues against toxicity was caused by sodium fluoride in rats. Carvacrol supplementation normalized all the anti‐oxidant enzymes and hepatic markers in NaF toxicity rats. Diphenyl‐1‐picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radical activities showed potent free‐radical scavenging activities. The study concluded that carvacrol modulated the anti‐oxidant enzymes and hepatic stress markers in NaF rats (Shanmugam et al., 2019). Carvacrol also protects from gastric ulcers and has become a worldwide health problem. A peptic ulcer is one of the gastric problems caused by Helicobacter pylori, smoking, stress, alcohol, and nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs (NSAID). A study investigated the gastroprotective effects of carvacrol in rodents in which NSAID, ischemia, and reperfusion made gastric lesions. The results demonstrated that carvacrol promoted a marked gastroprotection mediated by endogenous prostaglandins, increase in mucus production, KATP channels opening, NO synthase activation, and anti‐oxidant properties (Oliveira et al., 2012).
Carvacrol has significant protective effects in reducing the side effects of chemotherapeutics such as irinotecan hydrochloride anticancer drugs that cause induction of intestinal mucositis. Irinotecan hydrochloride triggers inflammation and leads to cell damaging via the transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, and member 1 receptor. Carvacrol reduced inflammatory biomarkers, such as nuclear factor κB and cyclooxygenase‐2, and levels of nitric oxides, malondialdehyde, and glutathione create oxidative stress. It also acts as an agonist of the transient receptor potential cation channel. Carvacrol also restored the tissue architecture of the villi and crypts in the small intestine and side by side improved the blood bacterial count, leukogram, body mass variation, and survival rate (Alvarenga et al., 2016). Arigesavan and Sudhandiran (2015) showed the anti‐inflammatory effects of carvacrol in the colon of Fischer 344 rats against inflammation induced by 1, 2‐dimethyl hydrazine plus dextran sodium sulfate. F344 rats were given three subcutaneous injections of DMH (40 mg/kg body wt) in the first week to F344 rats and free access to drinking water containing 1% DSS for the next 1 week was also given for 7–14 days as three cycles. 50 mg/kg body weight (o.p) carvacrol was administrated before and after tumor induction. Carvacrol‐treated groups suppress the inflammation in DMH/DSS‐induced animals, increased anti‐oxidant status; developed an endogenous anti‐oxidant system was observed and restorative histological lesions. Carvacrol also increased significantly the level of anti‐oxidant enzymes such as glutathione levels, superoxide dismutase, catalase, reduced nitric oxide, lipid peroxides, interleukin‐1 beta, and myeloperoxidase as compared to DMH/DSS induced rats (Arigesavan & Sudhandiran, 2015).
4. Immunomodulatory Role
Carvacrol action can modulate immune responses via different inflammatory parameters such as proliferation of T‐cells, isolated polymorph nuclear neutrophils IL‐2 and TNF‐α cytokines production, and ROS generating from whole blood phagocytes. Ezz‐Eldin et al. (2020) investigated the immunomodulatory effect of carvacrol against bronchial asthma induced by an intranasal dose of ovalbumin. It significantly caused a reduction in absolute eosinophil count, absolute eosinophil count, immunoglobulin E, inflammatory biomarkers (TNF‐α, L‐4, IL‐5, IL‐13, and interferon‐gamma), and enhancement in anti‐oxidant enzymes further that prevent from the inflammatory symptoms in asthma (Ezz‐Eldin et al., 2020). Combination of carvacrol with essential oils (Foeniculum vulgare, Saturea cuneifolia, and Origanum munitiflorum) can inhibit ROS production, T‐cells proliferation, and pro‐inflammatory cytokines (Khazdair et al., 2018; Orhan et al., 2016). Encapsulated carvacrol (250–650 μg/g) in necrotic enteritis animal disease caused by C. perfringens in chicken intestine prevented the immune‐mediated responses (Liu et al., 2016). Thymol and carvacrol in human mesenchymal stromal cells protect from oxidative stress‐related damage and cytotoxicity and preserve cell morphology (Bouhtit et al., 2019).
Tolerogenic dendritic cells (DCs) are a condition that leads to the induction of dampened pathogenic T cell responses and FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. Spiering et al. (2012) investigated the immunomodulatory properties of carvacrol by suppressing autoimmune arthritis in a mouse model. Amirghofran et al. (2016) also investigated carvacrol and thymol actions on DCs maturation and T cell activation. Both compounds also inhibited the mitogenic and allogeneic T‐cells responses and release of cytokines (Amirghofran et al., 2016). Carvacrol was also found to lower the vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM‐1), monocyte chemo‐attractant protein (MCP‐1), intracellular cell adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM‐1), interferon gamma‐induced protein 10, interferon‐inducible T‐cell alpha chemo‐attractant(I‐TAC), etc., as well as also decrease the remodeling biomarkers such as collagen I, III, epidermal growth factor receptor(EGFR), matrix metalloproteinase 1, and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (Han & Parker, 2017).
By investigating thymol and carvacrol (25 μg/ml) effects against Jurkat leukemia cells in in vitro models, Gholijani et al. in 2015 concluded that both compounds reduced IL‐2 and IFN‐γ production via downregulating AP‐1 and NFAT‐2 transcription factors (Gholijani et al., 2015). A study reported by Gandhi et al. found that carvacrol also regulates cytokine production, inhibits ROS accumulations, and inactivates eosinophils migration lungs. EO suppressed cytokine production, pro‐inflammatory and anti‐inflammatory mediators formation, and accumulation (Gandhi et al., 2020).
Carvacrol also protects in case of multiple sclerosis (MS) development by modulating pro‐ and anti‐inflammatory properties (TGF‐β, IL‐4, and IL‐10). Mahmoodi et al. (2019) studied carvacrol 5 and 10 mg/kg dose effect on auto‐immune encephalomyelitis and exhibited immune‐modulating actions on pro‐ and anti‐inflammatory cytokines. Carvacrol also improved pathological problems and improved clinical symptoms in patients (Gholijani & Amirghofran, 2016; Mahmoodi et al., 2019). Similarly, carvacrol (73 mg/kg) in combination with pomegranate (225 mg/kg/day) was studied against methotrexate (MTX)‐induced intestinal damage in 32 male Sprague–Dawley rats, using immunohistochemical and histopathological techniques (Türkcü et al., 2015). Carvacrol effects on cytokines genes expression in splenocytes of asthmatic mice were studied by Kianmehr et al. (2016) in rats in which asthma is induced by ovalbumin (OVA) and it was concluded that carvacrol significantly modulated the immune response by decreasing IL‐4, IL‐17, and TGF‐β gene expressions and increased IFN‐γ and FOXP3 (Kianmehr et al., 2016).
Khazdair and Boskabady (2019a, 2019b) investigated carvacrol effects on serum levels of interferon‐gamma (IFNγ), interleukins (IL‐2, IL‐4, IL‐6, IL‐8, and IL‐10), and pulmonary function tests in 22 patients exposed to sulfur mustard (SM) 27–30 years in a double‐blind manner for 2 months divided into placebo and carvacrol 1.2 mg/kg/day. It was concluded that carvacrol reduced inflammatory cytokines, while increased anti‐inflammatory cytokines and improved PFT tests in SM‐induced lung injury (Khazdair & Boskabady, 2019a, 2019b). Another study evaluated the immunomodulatory and ulcer protective action of carvacrol (25, 50 & 100 mg/kg) on an animal model in which gastric lesions were made by acetic acid. Results showed carvacrol gastric healing actions and also proved that it interferes with secretion and production of inflammatory mediators in case of ulcer (Hussein et al., 2019; Silva et al., 2012; Table 1).
4. Reproductive Role
Oxidative stress decreases the number of germ cells and damages testicular tubules, as reactive oxygen species (ROS) is very important for the sperm condensation, sperm‐oocyte fusion, and hyper‐activation required for normal fertilization, but excessive lipid peroxidation and ROS could damage sperm dysfunction and cause DNA damage and loss of motility. Oxidative stress leads to the damage of spermatozoa due to the lack of cytoplasmic defensive barriers and spermatozoon plasma membranes containing polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) get injured as well as destroy lipid structure in spermatozoa membranes and cause loss of motility and damage to membrane integrity. A study described by Shoorei et al. in 2019 investigated the role of carvacrol in 32 male adult Wistar rats in which diabetes was induced by streptozotocin (50 mg/kg) supplement. Findings suggested that carvacrol 75 mg/kg reduced the rate of germ cell apoptosis, reduced the activity of SOD and GPx enzymes, diminished the elevated levels of MDA, and improved morphology of the testis as well as decreased Bax and increased Bcl‐2 at the levels of gene and protein expression (Shoorei et al., 2019). A study conducted by Güvenç et al. (2019) found that carvacrol in combination with thymol has a significant impact on the quality of sperms improved by decreasing level of oxidative stress, MDA levels in testicles, liver, and kidney tissues, enhancing the GSH‐Px and catalase activities along with enhancement in spermatozoa concentration and motility (Güvenç et al., 2019). Moreover, carvacrol also improves the mean motility, movement characteristics, sperm capacitation, and fertilizing ability and prevents testicular damage (Cengİz et al., 2017). Carvacrol (25 and 50 mg/kg) prevented ketamine‐induced oxidative stress and damage in testicular tissues by lowering the level of MDA‐induced schizophrenia and increasing the anti‐oxidant enzymes (Araghi et al., 2017). Similarly, carvacrol prevents cyclophosphamide‐induced testis toxicity and damage in male rats due to its anti‐oxidative role (Cengiz et al., 2017). In adult male Sprague–Dawley rats, cisplatin induces reproductive toxicity by damaging the dermatological parameters (live sperm rate, motility, and abnormal sperm rate), increasing the oxidative stress, and inducing testicular degeneration whereas daily orally administrated carvacrol at the rate of 75 mg/kg prevented from these changes (Aksu et al., 2016).
New Paragraph
5. Conclusion
The purpose of this comprehensive review was to highlight and explain the biosynthesis mechanism of carvacrol and the significant protective effects of carvacrol as an anti‐oxidant, anticancer potential, anti‐inflammatory, antimicrobial, hepatoprotective effects, and neuro‐protective and anti‐obesity effects. Scientists and researchers have studied the potential of carvacrol and thymol for cancer prevention, diabetes prevention, wound healing, and immuno‐modulatory in vivo and in vitro assays. Carvacrol exhibits a high potential for the development of new therapeutic alternatives to cure human maladies. However, the extensive studies still required to elucidate the potential therapeutic effect of carvacrol on molecular level by involving long‐term human efficacy trial with special reference to its lethal dose, toxicity, and RDA.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge HEC for its support.
Notes
Imran, M. , Aslam, M. , Alsagaby, S. A. , Saeed, F. , Ahmad, I. , Afzaal, M. , Arshad, M. U. , Abdelgawad, M. A. , El‐Ghorab, A. H. , Khames, A. , Shariati, M. A. , Ahmad, A. , Hussain, M. , Imran, A. , & Islam, S. (2022). Therapeutic application of carvacrol: A comprehensive review. Food Science & Nutrition, 10, 3544–3561. 10.1002/fsn3.2994 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Author Contributions
Ali Imran, Email: moc.liamg@tf.narmiila.
Saiful Islam, Email: db.ca.ud@sfnilufias.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
- References
- Aksu, E. H. , Kandemir, F. M. , Altun, S. , Küçükler, S. , Çomaklı, S. , & Ömür, A. D. (2016). Ameliorative effect of carvacrol on cisplatin‐Induced reproductive damage in male rats. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 30(10), 513–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alagawany, M. , El‐Hack, M. A. , Farag, M. R. , Tiwari, R. , & Dhama, K. (2015). Biological effects and modes of action of carvacrol in animal and poultry pro‐duction and health‐a review. Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 3(2s), 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarenga, E. M. , Souza, L. K. , Araújo, T. S. , Nogueira, K. M. , Sousa, F. B. M. , Araújo, A. R. , Martins, C. S. , Pacífico, D. M. , Brito, G. A. , Souza, E. P. , & Sousa, D. P. (2016). Carvacrol reduces irinotecan‐induced intestinal mucositis through inhibition of inflammation and oxidative damage via TRPA1 receptor activation. Chemico‐Biological Interactions, 260, 129–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alves, Q. L. , Santos, P. V. , Santos, W. A. , Oliveira, S. C. , Jesus, R. L. , Froes, T. Q. , Castilho, M. S. , & Silva, D. F. (2016). Participation of trpm4/trpm7 channels in the cardiac activities of carvacrol on animals with essential hypertension. The FASEB Journal, 30(1_supplement), 942–944. [Google Scholar]
- Alzate, P. , Miramont, S. , Flores, S. , & Gerschenson, L. N. (2017). Effect of the potassium sorbate and carvacrol addition on the properties and antimicrobial activity of tapioca starch–Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose edible films. Starch‐Stärke, 69(5–6), 1600261. [Google Scholar]
- Amirghofran, Z. , Ahmadi, H. , Karimi, M. H. , Kalantar, F. , Gholijani, N. , & Malek‐Hosseini, Z. (2016). In vitro inhibitory effects of thymol and carvacrol on dendritic cell activation and function. Pharmaceutical Biology, 54(7), 1125–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, R. , & Akbari, M. (2018). The role of carvacrol as active compound of essential oils in diabetes. Applied Biological Sciences, 12, 583–586. [Google Scholar]
- Araghi, A. , Tabari, M. A. , & Golshahi, H. (2017). Protective effect of carvacrol on ketamine induced testicular damage in mouse model of schizophrenia. Journal of HerbMed Pharmacology, 6(3), 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ares, A. M. , Nozal, M. J. , Bernal, J. L. , & Bernal, J. (2020). Simultaneous determination of carvacrol and thymol in bee pollen by using a simple and efficient solvent extraction method and gas chromatography‐mass spectrometry. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 181, 113124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arigesavan, K. , & Sudhandiran, G. (2015). Carvacrol exhibits anti‐oxidant and anti‐inflammatory effects against 1, 2‐dimethyl hydrazine plus dextran sodium sulfate induced inflammation associated carcinogenicity in the colon of Fischer 344 rats. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 461(2), 314–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aristatile, B. , Al‐Assafa, A. H. , & Pugalendi, K. V. (2014). Carvacrol ameliorates the Ppar‐Α and cytochrome P450 Expression on D‐galactosamine induced hepatotoxicity rats. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines, 11(3), 118–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arunasree, K. (2010). Anti‐proliferative effects of carvacrol on a human metastatic breast cancer cell line, MDA‐MB 231. Phytomedicine, 17(8–9), 581–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakır, M. , Geyikoglu, F. , Colak, S. , Turkez, H. , Bakır, T. O. , & Hosseinigouzdagani, M. (2016). The carvacrol ameliorates acute pancreatitis‐induced liver injury via antioxidant response. Cytotechnology, 68(4), 1131–1146. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banik, S. , Akter, M. , Bondad, S. E. C. , Saito, T. , Hosokawa, T. , & Kurasaki, M. (2019). Carvacrol inhibits cadmium toxicity through combating against caspase dependent/independent apoptosis in PC12 cells. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 134, 110835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranauskaite, J. , Kubiliene, A. , Marksa, M. , Petrikaite, V. , Vitkevičius, K. , Baranauskas, A. , & Bernatoniene, J. (2017). The influence of different oregano species on the antioxidant activity determined using HPLC postcolumn DPPH method and anticancer activity of carvacrol and rosmarinic acid. BioMed Research International. 10.1155/2017/1681392 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Barnwal, P. , Vafa, A. , Afzal, S. M. , Shahid, A. , Hasan, S. K. , Alpashree, X. , & Sultana, S. (2018). Benzo (a) pyrene induces lung toxicity and inflammation in mice: Prevention by carvacrol. Human & Experimental Toxicology, 37(7), 752–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayir, A. G. , Kiziltan, H. S. , & Kocyigit, A. (2019). Plant family, carvacrol, and putative protection in gastric cancer. In Watson R. R (Ed.) Dietary interventions in gastrointestinal diseases (pp. 3–18). Elsevier. [Google Scholar]
- Bayramoglu, G. , Senturk, H. , Bayramoglu, A. , Uyanoglu, M. , Colak, S. , Ozmen, A. , & Kolankaya, D. (2014). Carvacrol partially reverses symptoms of diabetes in STZ‐induced diabetic rats. Cytotechnology, 66(2), 251–257. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaubrun, J. J.‐G. , Addy, N. , Keltner, Z. , Farris, S. , Ewing, L. , Gopinath, G. , & Hanes, D. E. (2018). Evaluation of the impact of varied carvacrol concentrations on Salmonella recovery in oregano and how corn oil can minimize the effect of carvacrol during preenrichment. Journal of Food Protection, 81(6), 977–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouhtit, F. , Najar, M. , Agha, D. M. , Melki, R. , Najimi, M. , Sadki, K. , Lewalle, P. , Hamal, A. , Lagneaux, L. , & Merimi, M. (2019). The biological response of mesenchymal stromal cells to thymol and carvacrol in comparison to their essential oil: An innovative new study. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 134, 110844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, F. O. , Silva, É. R. , Nunes, P. S. , Felipe, F. A. , Ramos, K. P. , Ferreira, L. A. S. , Lima, V. N. , Shanmugam, S. , Oliveira, A. S. , Guterres, S. S. , & Camargo, E. A. (2020). Effects of the solid lipid nanoparticle of carvacrol on rodents with lung injury from smoke inhalation. Naunyn‐Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology, 393(3), 445–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cengİz, M. , Tekİn, Y. , İnal, B. , & Ayhancı, A. (2017). Protective effects of carvacrol, essential composition of thyme plant, on cyclophosphamide‐induced reproductive system damage on rats. Türkiye Tarımsal Araștırmalar Dergisi, 4(2), 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Cengiz, M. , Teksoy, O. , Sahinturk, V. , Tekin, Y. , Gunes, S. , & Ayhanci, A. (2017). Ameliorative effects of carvacrol on cyclophosphamide‐induced testis damage and oxidative stress. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute Proceedings, 1(10), 1066. [Google Scholar]
- Cetik, S. , Ayhanci, A. , & Sahinturk, V. (2015). Protective effect of carvacrol against oxidative stress and heart injury in cyclophosphamide‐induced cardiotoxicity in rat. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 58(4), 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. , Ba, L. , Huang, W. , Liu, Y. , Pan, H. , Mingyao, E. , Shi, P. , Wang, Y. , Li, S. , Qi, H. , Sun, H. , & Cao, Y. (2017). Role of carvacrol in cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through activation of MAPK/ERK and Akt/eNOS signaling pathways. European Journal of Pharmacology, 796, 90–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S. , Choi, Y. , Park, S. , & Park, T. (2012). Carvacrol prevents diet‐induced obesity by modulating gene expressions involved in adipogenesis and inflammation in mice fed with high‐fat diet. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 23(2), 192–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chraibi, M. , Farah, A. , Elamin, O. , Iraqui, H. M. , & Benbrahim, K. F. (2020). Characterization, antioxidant, antimycobacterial, antimicrobial effects of Moroccan rosemary essential oil, and its synergistic antimicrobial potential with carvacrol. Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research, 11(1), 25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun, Y. L. , Kim, M. , Kim, Y. H. , Kim, N. , Yang, H. , Park, C. , Huh, Y. , & Jung, J. (2019). Carvacrol effectively protects demyelination by suppressing transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) in Schwann cells. Anatomical Science International, 5(95)1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churklam, W. , Chaturongakul, S. , Ngamwongsatit, B. , & Aunpad, R. (2020). The mechanisms of action of carvacrol and its synergism with nisin against Listeria monocytogenes on sliced bologna sausage. Food Control, 108, 106864. [Google Scholar]
- Cocolas, A. H. , Parks, E. L. , Ressler, A. J. , Havasi, M. H. , Seeram, N. P. , & Henry, G. E. (2019). Heterocyclic β‐keto sulfide derivatives of carvacrol: Synthesis and copper (II) ion reducing capacity. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 29(19), 126636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantas, B. P. V. , Alves, Q. L. , de Assis, K. S. , Ribeiro, T. P. , de Almeida, M. M. , de Vasconcelos, A. P. , de Araújo, D. A. , de Andrade Braga, V. , de Medeiros, I. A. , Alencar, J. L. , Silva, D. F. , & Alencar, J. L. (2015). Participation of the TRP channel in the cardiovascular effects induced by carvacrol in normotensive rat. Vascular Pharmacology, 67, 48–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Souza Polli, F. , Gomes, J. N. , Ferreira, H. S. , Santana, R. C. , & Fregoneze, J. B. (2019). Inhibition of salt appetite in sodium‐depleted rats by carvacrol: Involvement of noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways. European Journal of Pharmacology, 854, 119–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W. , Lu, H. , & Teng, J. (2013). Carvacrol attenuates diabetes‐associated cognitive deficits in rats. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 51(3), 813–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshafie, H. S. , Armentano, M. F. , Carmosino, M. , Bufo, S. A. , De Feo, V. , & Camele, I. (2017). Cytotoxic activity of Origanum vulgare L. on hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 and evaluation of its biological activity. Molecules, 22(9), 1435. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El‐Sayed, E. S. M. , Mansour, A. M. , & Abdul‐Hameed, M. S. (2016). Thymol and carvacrol prevent doxorubicin‐induced cardiotoxicity by abrogation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in rats. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 30(1), 37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel, J. B. , Heckler, C. , Tondo, E. C. , Daroit, D. J. , & da Silva Malheiros, P. (2017). Antimicrobial activity of free and liposome‐encapsulated thymol and carvacrol against Salmonella and Staphylococcus aureus adhered to stainless steel. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 252, 18–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezhumalai, M. , Ashokkumar, N. , & Pugalendi, K. V. (2015). Combination of carvacrol and rosiglitazone ameliorates high fat diet induced changes in lipids and inflammatory markers in C57BL/6J mice. Biochimie, 110, 129–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezhumalai, M. , Radhiga, T. , & Pugalendi, K. V. (2014). Antihyperglycemic effect of carvacrol in combination with rosiglitazone in high‐fat diet‐induced type 2 diabetic C57BL/6J mice. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 385(1–2), 23–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezz‐Eldin, Y. M. , Aboseif, A. A. , & Khalaf, M. M. (2020). Potential anti‐inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of carvacrol against ovalbumin‐induced asthma in rats. Life Sciences, 242, 117222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan, K. , Li, X. , Cao, Y. , Qi, H. , Li, L. , Zhang, Q. , & Sun, H. (2015). Carvacrol inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Anti‐Cancer Drugs, 26(8), 813–823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, L. M. , dos Santos Cruxen, C. E. , Bruni, G. P. , Fiorentini, Â. M. , da Rosa Zavareze, E. , Lim, L.‐T. , & Dias, A. R. G. (2019). Development of antimicrobial and antioxidant electrospun soluble potato starch nanofibers loaded with carvacrol. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 139, 1182–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, G. R. , Vasconcelos, A. B. S. , Haran, G. H. , da Silva Calisto, V. K. , Jothi, G. , Quintans, J. D. S. S. , Cuevas, L. E. , Narain, N. , Júnior, L. J. Q. , Cipolotti, R. , & Gurgel, R. Q. (2020). Essential oils and its bioactive compounds modulating cytokines: A systematic review on anti‐asthmatic and immunomodulatory properties. Phytomedicine, 73, 152854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gholami‐Ahangaran, M. , Ahmadi‐Dastgerdi, A. , Azizi, S. , Basiratpour, A. , Zokaei, M. , & Derakhshan, M. (2022). Thymol and carvacrol supplementation in poultry health and performance. Veterinary Medicine and Science, 8(1), 267–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gholijani, N. , Abolmaali, S. S. , Kalantar, K. , & Ravanrooy, M. H. (2020). Therapeutic effect of carvacrol‐loaded albumin nanoparticles on arthritic rats. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 19(1), 312–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gholijani, N. , Gharagozloo, M. , Farjadian, S. , & Amirghofran, Z. (2016). Modulatory effects of thymol and carvacrol on inflammatory transcription factors in lipopolysaccharide‐treated macrophages. Journal of Immunotoxicology, 13(2), 157–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gholijani, N. , Gharagozloo, M. , Kalantar, F. , Ramezani, A. , & Amirghofran, Z. (2015). Modulation of cytokine production and transcription factors activities in human Jurkat T cells by thymol and carvacrol. Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 5(Suppl 1), 653. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghorani, V. , Alavinezhad, A. , Rajabi, O. , Mohammadpour, A. H. , & Boskabady, M. H. (2021). Safety and tolerability of carvacrol in healthy subjects: A phase I clinical study. Drug and Chemical Toxicology, 44(2), 177–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilling, D. H. , Kitajima, M. , Torrey, J. , & Bright, K. R. (2014). Antiviral efficacy and mechanisms of action of oregano essential oil and its primary component carvacrol against murine norovirus. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 116(5), 1149–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, T. , Maciel, P. , Villanueva, L. , Santos, P. , Oliveira, I. J. , Veras, R. , Gonçalves, I. , & Medeiros, I. (2019). Carvacrol improves erectile dysfunction in spontaneously hypertensive rats , 125(5), 396–403. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2018.1476979. PMID: 29799283. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X. , Li, X. , Yang, X. , Yan, J. , Shi, P. , Ba, L. , Cao, Y. , Wang, P. , & Wang, P. (2019). The neuroprotective effects of carvacrol on ischemia/reperfusion‐induced hippocampal neuronal impairment by ferroptosis mitigation. Life Sciences, 235, 116795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarda, A. , Rubilar, J. F. , Miltz, J. , & Galotto, M. J. (2011). The antimicrobial activity of microencapsulated thymol and carvacrol. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 146(2), 144–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, A. G. , Scotti, L. , Scotti, M. T. , Júnior, F. J. M. , Melo, N. S. , Alves, R. S. , Júnior, W. D. , Bezerra, D. P. , Gelain, D. P. , & Júnior, L. J. Q. (2014). Evidence for the involvement of descending pain‐inhibitory mechanisms in the attenuation of cancer pain by carvacrol aided through a docking study. Life Sciences, 116(1), 8–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gursul, S. , Karabulut, I. , & Durmaz, G. (2019). Antioxidant efficacy of thymol and carvacrol in microencapsulated walnut oil triacylglycerols. Food Chemistry, 278, 805–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güvenç, M. , Cellat, M. , Gökçek, İ. , Yavaş, İ. , & Yurdagül Özsoy, Ş. (2019). Effects of thymol and carvacrol on sperm quality and oxidant/antioxidant balance in rats. Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry, 125(5), 396–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han, X. , & Parker, T. L. (2017). Anti‐inflammatory, tissue remodeling, immunomodulatory, and anticancer activities of oregano (Origanum vulgare) essential oil in a human skin disease model. Biochimie Open, 4, 73–77. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidarian, E. , & Keloushadi, M. (2019). Antiproliferative and anti‐invasion effects of carvacrol on PC3 human prostate cancer cells through reducing pSTAT3, pAKT, and pERK1/2 signaling proteins. International Journal of Preventive Medicine, 10(1), 156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D. , Choi, B. , Kho, A. , Lee, S. , Jeong, J. , Kang, B. , Kang, D. H. , Park, K. H. , & Suh, S. (2018). Carvacrol attenuates hippocampal neuronal death after global cerebral ischemia via inhibition of transient receptor potential melastatin 7. Cell, 7(12), 231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta, M. , Nakata, R. , Katsukawa, M. , Hori, K. , Takahashi, S. , & Inoue, H. (2010). Carvacrol, a component of thyme oil, activates PPARα and γ and suppresses COX‐2 expression. Journal of Lipid Research, 51(1), 132–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou, N. , Mai, Y. , Qiu, X. , Yuan, W. , Li, Y. , Luo, C. , Liu, Y. , Zhang, G. , Zhao, G. , & Luo, J.‐D. (2019a). Carvacrol attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy by modulating the PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 pathway in diabetic mice. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 10, 998. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou, N. , Mai, Y. , Qiu, X. , Yuan, W. , Li, Y. , Luo, C. , Liu, Y. , Zhang, G. , Zhao, G. , & Luo, J.‐D. (2019b). The therapeutic effect of nano‐encapsulated and nano‐emulsion forms of carvacrol on experimental liver fibrosis. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 90, 880–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, K. , Friedrich, L. , Kisko, G. , Ayari, E. , Nemeth, C. , & Dalmadi, I. (2019). Use of allyl‐isothiocyanate and carvacrol to preserve fresh chicken meat during chilling storage. Czech Journal of Food Sciences, 37(6), 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Iannitelli, A. , Grande, R. , Stefano, A. D. , Giulio, M. D. , Sozio, P. , Bessa, L. J. , Laserra, S. , Paolini, C. , Protasi, F. , & Cellini, L. (2011). Potential antibacterial activity of carvacrol‐loaded poly(DL‐lactide‐co‐glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles against microbial biofilm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(8), 5039–5051. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamali, T. , Kavoosi, G. , & Ardestani, S. K. (2020). In‐vitro and in‐vivo anti‐breast cancer activity of OEO (Oliveria decumbens vent essential oil) through promoting the apoptosis and immunomodulatory effects. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 248, 112313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamhiri, M. , Safi Dahej, F. , Astani, A. , Hejazian, S. H. , Hafizibarjin, Z. , Ghobadi, M. , Moradi, A. , Khoradmehr, A. , & Safari, F. (2019). Carvacrol ameliorates pathological cardiac hypertrophy in both in‐vivo and in‐vitro models. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 18(3), 1380–1394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G. , Whaley‐Connell, A. , & Sowers, J. R. (2018). Diabetic cardiomyopathy: A hyperglycaemia‐and insulin‐resistance‐induced heart disease. Diabetologia, 61(1), 21–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karam, L. , Roustom, R. , Abiad, M. G. , El‐Obeid, T. , & Savvaidis, I. N. (2019). Combined effects of thymol, carvacrol and packaging on the shelf‐life of marinated chicken. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 291, 42–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F. , Khan, I. , Farooqui, A. , & Ansari, I. A. (2017). Carvacrol induces reactive oxygen species (ROS)‐mediated apoptosis along with cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 in human prostate cancer cells. Nutrition and Cancer, 69(7), 1075–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F. , Singh, V. K. , Saeed, M. , Kausar, M. A. , & Ansari, I. A. (2019). Carvacrol induced program cell death and cell cycle arrest in androgen‐independent human prostate cancer cells via inhibition of notch signaling. Anti‐Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry (Formerly Current Medicinal Chemistry‐Anti‐Cancer Agents), 19(13), 1588–1608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I. , Bahuguna, A. , Kumar, P. , Bajpai, V. K. , & Kang, S. C. (2017). Antimicrobial potential of carvacrol against uropathogenic Escherichia coli via membrane disruption, depolarization, and reactive oxygen species generation. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 2421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I. , Bhardwaj, M. , Shukla, S. , Lee, H. , Oh, M.‐W. , Bajpai, V. K. , Huh, Y. S. , & Kang, S. C. (2019). Carvacrol encapsulated nanocarrier/nanoemulsion abrogates angiogenesis by downregulating COX‐2, VEGF and CD31 in vitro and in vivo in a lung adenocarcinoma model. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 181, 612–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I. , Bhardwaj, M. , Shukla, S. , Min, S.‐H. , Choi, D. K. , Bajpai, V. K. , Huh, Y. S. , & Kang, S. C. (2019). Carvacrol inhibits cytochrome P450 and protects against binge alcohol‐induced liver toxicity. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 131, 110582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S. T. , Khan, M. , Ahmad, J. , Wahab, R. , Abd‐Elkader, O. H. , Musarrat, J. , Alkhathlan, H. Z. , & Al‐Kedhairy, A. A. (2017). Thymol and carvacrol induce autolysis, stress, growth inhibition and reduce the biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans . AMB Express, 7(1), 1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazdair, M. R. , & Boskabady, M. H. (2019a). A double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled clinical trial on the effect of carvacrol on serum cytokine levels and pulmonary function tests in sulfur mustard induced lung injury. Cytokine, 113, 311–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazdair, M. R. , & Boskabady, M. H. (2019b). The effect of carvacrol on inflammatory mediators and respiratory symptoms in veterans exposed to sulfur mustard, a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Respiratory Medicine, 150, 21–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazdair, M. R. , Ghorani, V. , Alavinezhad, A. , & Boskabady, M. H. (2018). Pharmacological effects of Zataria multiflora Boiss L. and its constituents focus on their anti‐inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology, 32(1), 26–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kianmehr, M. , Rezaei, A. , & Boskabady, M. H. (2016). Effect of carvacrol on various cytokines genes expression in splenocytes of asthmatic mice. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 19(4), 402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N. H. , Cho, T. J. , & Rhee, M. S. (2017). Sodium chloride does not ensure microbiological safety of foods: Cases and solutions. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 101, 1–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein, A. H. , Carstens, M. I. , & Carstens, E. (2013). Eugenol and carvacrol induce temporally desensitizing patterns of oral irritation and enhance innocuous warmth and noxious heat sensation on the tongue. PAIN®, 154(10), 2078–2087. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B. , Yeom, M. , Shim, I. , Lee, H. , & Hahm, D.‐H. (2020). Inhibitory effect of carvacrol on lipopolysaccharide‐induced memory impairment in rats. The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology, 24(1), 27–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. H. , Kim, Y. G. , & Lee, J. (2017). Carvacrol‐rich oregano oil and thymol‐rich thyme red oil inhibit biofilm formation and the virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli . Journal of Applied Microbiology, 123(6), 1420–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K. P. , Sudjarwo, G. W. , Jung, S. H. , Lee, D. , Lee, D.‐Y. , Lee, G. B. , Baek, S. , Kim, D. Y. , Lee, H. M. , Kim, B. , & Kwon, S. C. (2015). Carvacrol inhibits atherosclerotic neointima formation by downregulating reactive oxygen species production in vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis, 240(2), 367–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. , Xu, J. Z. , Gu, C. X. , Liu, G. L. , & Tian, K. (2019). Carvacrol suppresses inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast‐like synoviocytes. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 120(5), 8169–8176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim, W. , Ham, J. , Bazer, F. W. , & Song, G. (2019). Carvacrol induces mitochondria‐mediated apoptosis via disruption of calcium homeostasis in human choriocarcinoma cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234(2), 1803–1815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima, T. C. , Da Nóbrega, F. R. , De Brito, A. E. M. , & De Sousa, D. P. (2017). Analgesic‐like activity of essential oil constituents: An update. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F. , Saricaoglu, F. T. , Avena‐Bustillos, R. J. , Bridges, D. F. , Takeoka, G. R. , Wu, V. C. , Chiou, B. S. , Wood, D. F. , McHugh, T. H. , Zhong, F. , & Zhong, F. (2018). Antimicrobial carvacrol in solution blow‐spun fish‐skin gelatin nanofibers. Journal of Food Science, 83(4), 984–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. , Diarra, M. S. , Zhang, Y. , Wang, Q. , Yu, H. , Nie, S.‐P. , Xie, M. Y. , & Gong, J. (2016). Effect of encapsulated carvacrol on the incidence of necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens. Avian Pathology, 45(3), 357–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. , Wei, J. , Ma, K.‐T. , Li, C.‐L. , Mai, Y.‐P. , Qiu, X.‐X. , Wei, H. , Hou, N. , & Luo, J.‐D. (2020). Carvacrol protects against diabetes‐induced hypercontractility in the aorta through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 125, 109825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llana‐Ruiz‐Cabello, M. , Maisanaba, S. , Puerto, M. , Prieto, A. I. , Pichardo, S. , Moyano, R. , Prieto, A. I. , González‐Pérez, J. A. , & Cameán, A. M. (2016). Genotoxicity evaluation of carvacrol in rats using a combined micronucleus and comet assay. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 98, 240–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoodi, M. , Amiri, H. , Ayoobi, F. , Rahmani, M. , Taghipour, Z. , Ghavamabadi, R. T. , Jafarzadeh, A. , & Sankian, M. (2019). Carvacrol ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through modulating pro‐and anti‐inflammatory cytokines. Life Sciences, 219, 257–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manouchehrabadi, M. , Farhadi, M. , Azizi, Z. , & Torkaman‐Boutorabi, A. (2020). Carvacrol protects against 6‐hydroxydopamine‐induced neurotoxicity in in vivo and in vitro models of Parkinson's disease. Neurotoxicity Research, 37(1), 156–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazarei, Z. , & Rafati, H. (2019). Nanoemulsification of Satureja khuzestanica essential oil and pure carvacrol; comparison of physicochemical properties and antimicrobial activity against food pathogens. LWT, 100, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Memar, M. Y. , Raei, P. , Alizadeh, N. , Aghdam, M. A. , & Kafil, H. S. (2017). Carvacrol and thymol: Strong antimicrobial agents against resistant isolates. Reviews in Medical Microbiology, 28(2), 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Miladi, H. , Zmantar, T. , Chaabouni, Y. , Fedhila, K. , Bakhrouf, A. , Mahdouani, K. , & Chaieb, K. (2016). Antibacterial and efflux pump inhibitors of thymol and carvacrol against food‐borne pathogens. Microbial Pathogenesis, 99, 95–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milovanović, M. , Milosavljević, M. , Đorđe, M. S. , Trailović, S. , Vučinić, M. , Trailović, J. N. , Marković, M. , & Đurđević, D. (2016). The effect of carvacrol on inflammatory pain and motor coordination in rats. Acta Veterinaria, 66(4), 478–488. [Google Scholar]
- Mir, M. , Permana, A. D. , Ahmed, N. , Khan, G. M. , ur Rehman, A. , & Donnelly, R. F. (2020). Enhancement in site‐specific delivery of carvacrol for potential treatment of infected wounds using infection responsive nanoparticles loaded into dissolving microneedles: A proof of concept study. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 147, 57–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monzote, L. , Geroldinger, G. , Tonner, M. , Scull, R. , De Sarkar, S. , Bergmann, S. , Bacher, M. , Staniek, K. , Chatterjee, M. , Rosenau, T. , & Gille, L. (2018). Interaction of ascaridole, carvacrol, and caryophyllene oxide from essential oil of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. with mitochondria in Leishmania and other eukaryotes. Phytotherapy Research, 32(9), 1729–1740. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S. , Schmidt, A.‐M. , Escher, U. , Kittler, S. , Kehrenberg, C. , Thunhorst, E. , Bereswill, S. , & Heimesaat, M. M. (2020). Carvacrol ameliorates acute campylobacteriosis in a clinical murine infection model. Gut Pathogens, 12(1), 1–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, I. S. , da Silva, F. V. , Viana, A. F. S. , dos Santos, M. R. , Quintans‐Júnior, L. J. , Maria do Carmo, C. M. , Nunes, P. , Oliveira, F. , & Oliveira, R. C. M. (2012). Gastroprotective activity of carvacrol on experimentally induced gastric lesions in rodents. Naunyn‐Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology, 385(9), 899–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, I. E. , Mesaik, M. A. , Jabeen, A. , & Kan, Y. (2016). Immunomodulatory properties of various natural compounds and essential oils through modulation of human cellular immune response. Industrial Crops and Products, 81, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Pakdemirli, A. , Karaca, C. , Sever, T. , Daşkin, E. , Leblebici, A. , Yiğitbaşi, T. , & Başbinar, Y. (2020). Carvacrol alters soluble factors in HCT‐116 and HT‐29 cell lines. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences, 50(1), 271–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palabiyik, S. , Karakus, E. , Halici, Z. , Cadirci, E. , Bayir, Y. , Ayaz, G. , & Cinar, I. (2016). The protective effects of carvacrol and thymol against paracetamol–induced toxicity on human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (HepG2). Human & Experimental Toxicology, 35(12), 1252–1263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto‐Neves, D. , Silva‐Alves, K. , Gomes, M. , Lima, F. , Lahlou, S. , Magalhães, P. , Ceccatto, V. M. , Coelho‐de‐Souza, A. N. , & Leal‐Cardoso, J. (2010). Vasorelaxant effects of the monoterpenic phenol isomers, carvacrol and thymol, on rat isolated aorta. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology, 24(3), 341–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilau, M. R. , Alves, S. H. , Weiblen, R. , Arenhart, S. , Cueto, A. P. , & Lovato, L. T. (2011). Antiviral activity of the Lippia graveolens (Mexican oregano) essential oil and its main compound carvacrol against human and animal viruses. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 42(4), 1616–1624. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potočnjak, I. , & Domitrović, R. (2016). Carvacrol attenuates acute kidney injury induced by cisplatin through suppression of ERK and PI3K/Akt activation. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 98, 251–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potočnjak, I. , Gobin, I. , & Domitrović, R. (2018). Carvacrol induces cytotoxicity in human cervical cancer cells but causes cisplatin resistance: Involvement of MEK–ERK activation. Phytotherapy Research, 32(6), 1090–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeini, A. S. , Hafizibarjin, Z. , Rezvani, M. E. , Safari, F. , Aghda, F. A. , & Mehrjerdi, F. Z. (2019). Carvacrol suppresses learning and memory dysfunction and hippocampal damages caused by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Naunyn‐Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology, 393(4), 581–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rezvi, F. B. , & Roy, A. (2019). Carvacrol: A well‐known phytochemical for modern dentistry. Drug Invention Today, 11(6), 1460–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, C. T. , Gasparotto, J. , Petiz, L. L. , Brum, P. O. , Peixoto, D. O. , Kunzler, A. , da‐Rosa Silva, H. , Bortolin, R. C. , Almeida, R. F. , Quintans Quintans‐Junior, L. , & Araújo, A. A. (2019). Oral administration of carvacrol/β‐cyclodextrin complex protects against 6‐hydroxydopamine‐induced dopaminergic denervation. Neurochemistry International, 126, 27–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez‐Garcia, I. , Silva‐Espinoza, B. , Ortega‐Ramirez, L. A. , Leyva, J. M. , Siddiqui, M. W. , Cruz‐Valenzuela, M. R. , Gonzalez‐Aguilar, G. A. , & Ayala‐Zavala, J. F. (2016). Oregano essential oil as an antimicrobial and antioxidant additive in food products. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 56(10), 1717–1727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolim, M. D. O. P. , de Almeida, A. R. , da Rocha Pitta, M. G. , de Melo Rêgo, M. J. B. , Quintans‐Júnior, L. J. , de Souza Siqueira Quintans, J. , Heimfarth, L. , Scotti, L. , Scotti, M. T. , da Cruz, R. M. D. , de Almeida, R. N. , da Silva, T. G. , de Oliveira, J. A. , de Campos, M. L. , Marchand, P. , & Mendonça‐Junior, F. J. B. (2019). Design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of CVIB, a codrug of carvacrol and ibuprofen as a novel anti‐inflammatory agent. International Immunopharmacology, 76, 105856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghzadeh, S. , Hejazian, S. H. , Jamhiri, M. , Hafizibarjin, Z. , Sadeghzadeh, S. , & Safari, F. (2018). The effect of carvacrol on transcription levels of Bcl‐2 family proteins in hypertrophied heart of rats. Physiology and Pharmacology, 22(1), 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Samarghandian, S. , Azimi‐Nezhad, M. , & Farkhondeh, T. (2016). Preventive effect of carvacrol against oxidative damage in aged rat liver. International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research, 87 (1–2), 59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarghandian, S. , Farkhondeh, T. , Samini, F. , & Borji, A. (2016). Protective effects of carvacrol against oxidative stress induced by chronic stress in rat's brain, liver, and kidney. Biochemistry Research International, 2016, 2645237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaffaro, R. , Maio, A. , & Nostro, A. (2020). Poly (lactic acid)/carvacrol‐based materials: Preparation, physicochemical properties, and antimicrobial activity. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 104(5), 1823–1835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabir, H. , Kundu, S. , Basir, S. F. , & Khan, L. A. (2014). Modulation of Pb (II) caused aortal constriction by eugenol and carvacrol. Biological Trace Element Research, 161(1), 116–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahrokhi Raeini, A. , Zare Mehrjerdi, F. , & Afkhami Aghda, F. (2018). P43: The effect of carvacrol on blood pressure and some blood parameters in lead‐exposed rats. The Neuroscience Journal of Shefaye Khatam, 6(2), 74. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, K. R. , Siva, M. , Ravi, S. , Shanmugam, B. , & Reddy, K. S. (2019). Bioactive compound of Ocimum sanctum carvacrol supplementation attenuates fluoride toxicity in sodium fluoride intoxicated rats: A study with respect to clinical aspect. Pharmacognosy Magazine, 15(62), 144. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi‐Rad, M. , Varoni, E. , Iriti, M. , Martorell, M. , Setzer, W. , del‐Mar Contreras, M. , Salehi, B. , Soltani‐Nejad, A. , Rajabi, S. , Tajbakhsh, M. , & Sharifi‐Rad, J. (2018). Carvacrol and human health: A comprehensive review. Phytotherapy Research, 32(9), 1675–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoorei, H. , Khaki, A. , Khaki, A. A. , Hemmati, A. A. , Moghimian, M. , & Shokoohi, M. (2019). The ameliorative effect of carvacrol on oxidative stress and germ cell apoptosis in testicular tissue of adult diabetic rats. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 111, 568–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva, F. V. , Guimaraes, A. G. , Silva, E. R. , Sousa‐Neto, B. P. , Machado, F. D. , Quintans‐Júnior, L. J. , Arcanjo, D. D. , Oliveira, F. A. , & Oliveira, R. C. (2012). Anti‐inflammatory and anti‐ulcer activities of carvacrol, a monoterpene present in the essential oil of oregano. Journal of Medicinal Food, 15(11), 984–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J. C. , Almeida, J. R. , Quintans, J. S. , Gopalsamy, R. G. , Shanmugam, S. , Serafini, M. R. , Oliveira, M. R. , Silva, B. , Martins, A. , Castro, F. F. , & Menezes, I. R. (2016). Enhancement of orofacial antinociceptive effect of carvacrol, a monoterpene present in oregano and thyme oils, by β‐cyclodextrin inclusion complex in mice. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 84, 454–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siroli, L. , Braschi, G. , de Jong, A. , Kok, J. , Patrignani, F. , & Lanciotti, R. (2018). Transcriptomic approach and membrane fatty acid analysis to study the response mechanisms of Escherichia coli to thyme essential oil, carvacrol, 2‐(E)‐hexanal and citral exposure. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 125(5), 1308–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somensi, N. , Rabelo, T. K. , Guimarães, A. G. , Quintans‐Junior, L. J. , de Souza Araújo, A. A. , Moreira, J. C. F. , & Gelain, D. P. (2019). Carvacrol suppresses LPS‐induced pro‐inflammatory activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages through ERK1/2 and NF‐kB pathway. International Immunopharmacology, 75, 105743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song, X. , Chen, A. , Liu, Y. , Wang, X. , Zhou, Y. , Liu, L. , Zhang, X. , Wang, L. , & Yang, P. (2013). Carvacrol pretreatment attenuates myocardial oxidative stress and apoptosis following myocardial ischemia‐reperfusion in mice. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 33(11), 1624–1627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalletta, S. , Flati, V. , Toniato, E. , Di Gregorio, J. , Marino, A. , Pierdomenico, L. , Marchisio, M. , D'Orazi, G. , Cacciatore, I. , & Robuffo, I. (2018). Carvacrol reduces adipogenic differentiation by modulating autophagy and ChREBP expression. PLoS One, 13(11), e0206894. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiering, R. , Van Der Zee, R. , Wagenaar, J. , Kapetis, D. , Zolezzi, F. , Van Eden, W. , & Broere, F. (2012). Tolerogenic dendritic cells that inhibit autoimmune arthritis can be induced by a combination of carvacrol and thermal stress. PLoS One, 7(9), e46336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stojanović, N. M. , Stevanović, M. , Randjelović, P. , Petrović, V. , Sokolović, D. , Mitić, K. , Mladenović, B. , Lalić, J. , & Radulović, N. (2018). Toxicity of carvacrol and its potential in preventing L‐arginine‐induced pancreatic damage. Facta Universitatis, Series Physics, Chemistry and Technology, 16(1), 160. [Google Scholar]
- Suganthi, R. U. , & Manpal, S. (2013). Biological and pharmacological of actions carvacrol and its effects on poultry: An updated review. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2(2013), 3581–3595. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X. , Cameron, R. G. , & Bai, J. (2020). Effect of spray‐drying temperature on physicochemical, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of pectin/sodium alginate microencapsulated carvacrol. Food Hydrocolloids, 100, 105420. [Google Scholar]
- Suntres, Z. E. , Coccimiglio, J. , & Alipour, M. (2015). The bioactivity and toxicological actions of carvacrol. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 55(3), 304–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tampau, A. , González‐Martínez, C. , & Chiralt, A. (2020). Biodegradability and disintegration of multilayer starch films with electrospun PCL fibres encapsulating carvacrol. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 173(6), 109100. [Google Scholar]
- Tas, B. A. , Sehit, E. , Tas, C. E. , Unal, S. , Cebeci, F. C. , Menceloglu, Y. Z. , & Unal, H. (2019). Carvacrol loaded halloysite coatings for antimicrobial food packaging applications. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 20, 100300. [Google Scholar]
- Tohidi, B. , Rahimmalek, M. , Arzani, A. , & Sabzalian, M. R. (2020). Thymol, carvacrol, and antioxidant accumulation in Thymus species in response to different light spectra emitted by light‐emitting diodes. Food Chemistry, 307, 125521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trindade, G. G. G. , Thrivikraman, G. , Menezes, P. P. , França, C. M. , Lima, B. S. , Carvalho, Y. M. B. G. , Souza, E. P. B. S. S. , Duarte, M. C. , Shanmugam, S. , Quintans‐Júnior, L. J. , Bezerra, D. P. , Bertassoni, L. E. , & Araújo, A. A. S. (2019). Carvacrol/β‐cyclodextrin inclusion complex inhibits cell proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 125, 198–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Türkcü, G. , Alabalık, U. , Keleş, A. N. , Bozkurt, M. , İbiloğlu, İ. , Fırat, U. , & Büyükbayram, H. (2015). Protective effects of carvacrol and pomegranate against methotrexate‐induced intestinal damage in rats. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 8(9), 15474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimalanathan, S. , & Hudson, J. (2012). Anti‐Influenza virus activities of commercial oregano oils and their carriers. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 2(7), 214. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P. , & Wu, Y. (2021). A review on colloidal delivery vehicles using carvacrol as a model bioactive compound. Food Hydrocolloids, 120, 106922. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. , Song, X. , Yang, P. , Liu, Y. , Wang, L. , Liu, L. , Qu, L. , & Chen, A. H. (2013). Carvacrol pretreatment attenuates mitochondrial damage during myocardial ischemia‐reperfusion in mice. Journal of Tropical Medicine, 13(6), 674–677. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.‐K. , Xue, H.‐X. , Zhou, Z. , & Peng, J. (2017). A carvacrol–thymol blend decreased intestinal oxidative stress and influenced selected microbes without changing the messenger RNA levels of tight junction proteins in jejunal mucosa of weaning piglets. Animal, 11(2), 193–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q. H. , Yan, F. X. , Zu, X. Y. , Wu, Y. H. , Wu, X. P. , Liao, M. C. , Deng, S. W. , Yin, L. L. , & Zhuang, Y. Z. (2012). Anti‐proliferative and pro‐apoptotic effect of carvacrol on human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG‐2. Cytotechnology, 64(1), 43–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W. , Liu, Q. , & Zhu, S. (2013). Carvacrol protects against acute myocardial infarction of rats via anti‐oxidative and anti‐apoptotic pathways. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 36(4), 579–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeytun, H. , & Özkorkmaz, E. G. (2021). Effects of carvacrol in an experimentally induced esophageal burn model: Expression of VEGF and Caspase‐3 proteins. Journal of Investigative Surgery, 34(4), 408–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zotti, M. , Colaianna, M. , Morgese, M. , Tucci, P. , Schiavone, S. , Avato, P. , & Trabace, L. (2013). Carvacrol: From ancient flavoring to neuromodulatory agent. Molecules, 18(6), 6161–6172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
3.6. Antiprolifertive and Citotoxic Activity of Essential Oils of Oregano
Essential oil constituents could exert antiproliferative effect. Different mechanisms such antioxidant, antimutagenic, antiproliferative, among others are responsible for their chemopreventive properties [155] The antiproliferative effects of EOs have been demonstrated in diverse cancer cell models through several pathways [156].
Marrelli et al. [117] studied the antiproliferative activity of EOs of Origanum species. At 100 µg/mL concentration, EOs derived from O. dictamnus showed the most interesting biological activity with an inhibition on colon carcinoma cell line (LoVo) of 58.39% after 24 h. Additionally, the IC50 value for this essential oil was 84.76 µg/mL after 24 h and 72.26 µg/mL after 48 h of treatment. In the same study, it was reported that the EOs from O. dictamnus and O. libanoticum had an antiproliferative activity of 49.83% and 48.50% in the hepatocarcinoma cell line (HepG2) at 100 µg/mL concentration. Begnini et al. [157] showed that EOs from O. vulgare inhibit cell proliferation in human breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7), and human colon adenocarcinoma (HT-29) cells at 50 mg/mL (60.8% and 48.9%, respectively).However, an increase in the EOO concentration did not increase the cell growth inhibition. The authors implied that the effect could be attributed to the main components (terpinen-4-ol, thymol, γ-terpinene and carvacrol). Besides, EOs of O. hirtum significantly reduced the proliferation of human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial (A549) cell line, after 24 h incubation, compared with untreated control cells [76]. Furthermore, it was suggested that the EOO modifies the onset of mitosis, possibly prior to the G2 phase and prophase.
Many evidences have shown that EOO had antitumor effect. EOO have shown antitumor activity both in in vivo and in vitro assays. An in vivo study reported that low doses of EOO in a three-month period exerted preventive action by decreasing the sizes of tumors by 1.5 times in diseased animals. It was suggested that the EOO could possible affect the development and progression of the tumor process via the activation of regulator cell molecules [158]. The in vitro antitumor activity of EOs of O. onites, was analyzed against rat adipose tissue endothelial cells and c-H-ras transformed rat embryonic fibroblasts (5RP7) cells. EOO at 125, 250 and 500 µg/mL resulted in significant inhibition of cell viability. In addition, EOO induced apoptosis of 5RP7 cells and blocked in vitro tube formation which accounts for its angiogenic activity [159].
Besides, EOO have shown activity against genotoxic agents, which are capable of altering DNA and thereby causing cancer or mutation [160]. The effects of AFB1 (5 µM), a cancer promotor, on human peripheral lymphocytes, were decreased after treatment with EOs of O. rotundifolium (1.5 µL and 2.0 µL). This activity could be attributed in part to the EO composition and its antioxidant capacity [161]. Similarly, the combined treatment of prallethrin and EOs from O. majorana in bone marrow cells of rats, resulted in the reduction of the chromosomal aberration (54.54%), thus, EOO demonstrated to have genotoxic effect. The effects could be attributed to the scavenge ability of EOO and its contribution in hindering lipid peroxidation [162].
Furthermore, in human breast (MCF-7) and prostate (LNCaP) cancer cell lines, EOs of O. majorana and O. vulgare showed an inhibitory effect on cancer cell viability in a range of 79–88% at 0.5 mg/mL (24 h). Origanum majorana was more cytotoxic than O. vulgare against MCF-7 and LNCaP cells with IC50s of 70.0 and 85.3 µg/mL [163]. Similarly, cytotoxicity of EOs was tested using human keratinocyte (HaCaT) and lung cancer (A549) cell lines. Cell viability decreased in a concentration-dependent manner on both cell lines. Essential oils of O. hirtum exhibited cytotoxicity both on HaCaT and A549 cells with IC50 values ranging from 146.8 to 148.8 μg/mL and from 147.1 to 177.1 μg/mL respectively, after 24, 48 and 72 h [80]. In another study, EOs of O. compactum have shown to be non-toxic towards MCF-7 cells (IC50 > 100 mg/L) [111].
Essential oils from oregano have been proposed as dietary inhibitors of mutagenesis and carcinogenesis [162]. Nonetheless, investigations about anticarcinogenic effect of EOO are scarce. Likewise, there are considerably fewer works dedicated to the biological activity of EOs using cell cultures and using in vivo models [158]. Furthermore, the molecular targets at the genome level and the involved genetic pathways of the mechanisms of EOO are remaining poorly explored [164].
A brief compilation of the biological activities, mentioned above, of EOs from different species of oregano is shown in Table 2.



